Art Making and Exhibiting (formally known as VCE Studio Arts)
Prerequisites
There are no prerequisites for entry to Units 1, 2 and 3. Students must undertake Unit 3 and Unit 4 as a sequence. Taking 10 Studio Arts or any of the other Visual Arts subjects is highly advisable.
Overview
VCE Art Making and Exhibiting introduces students to art creation and exhibition methods. Through inquiry learning, students explore materials, techniques, processes, and the ways artworks are made. They learn how art elements and principles contribute to aesthetic qualities and convey ideas visually. Students develop their skills through creating and presenting their own artworks, as well as analysing artworks by other artists. Visiting exhibitions is essential to understanding display and curation practices, influencing students’ own art. Responding to artworks in various spaces, such as galleries and museums, is integral to the study. Students gain insights into exhibition design, conservation, and promotion, while appreciating the diversity and different forms of art. They also learn about curating, displaying, and conserving their own and others’ artworks. Students become aware of difference and diversity in the views of others working in the arts industry, giving them a stronger understanding of the various forms that art may take.
What type of projects to expect?
Folio documentation of the production process; artwork production, e.g. paintings, drawings, prints, sculptures, ceramics, analogous and/or digital photography; experimentation with a variety of materials and techniques associated with specific artforms; visual analysis tasks.
What future pathways there exist?
VCE Art Making and Exhibiting provides pathways to tertiary courses in e.g. Fine Arts, Art History, Art Curatorship, Art Therapy, Advertising and Marketing.
Course Description
Unit 1: Semester 1 – Explore, expand and investigate
In this unit students explore materials, techniques and processes in a range of art forms. They expand their knowledge and understanding of the characteristics, properties and application of materials used in art making. They explore selected materials to understand how they relate to specific art forms and how they can be used in the making of artworks. Students also explore the historical development of specific art forms and investigate how the characteristics, properties and use of materials and techniques have changed over time. Throughout their investigation students become aware of and understand the safe handling of materials they use.
Students explore the different ways artists use materials, techniques and processes. The students’ exploration and experimentation with materials and techniques stimulates ideas, inspires different ways of working and enables a broad understanding of the specific art forms. Their exploration and experimentation is documented in both visual and written form in a Visual Arts journal.
ASSESSMENT
1. Folios (65%)
2. Research (15%)
3. Examination (20%)
Unit 2: Semester 2 – Understand, develop and resolve
In this unit students continue to research how artworks are made by investigating how artists use aesthetic qualities to represent ideas in artworks. They broaden their investigation to understand how artworks are displayed to audiences, and how ideas are represented to communicate meaning.
Students respond to a set theme and progressively develop their own ideas. Students learn how to develop their ideas using materials, techniques and processes, and art elements and art principles. They consolidate these ideas to plan and make finished artworks, reflecting on their knowledge and understanding of the aesthetic qualities of artworks. The planning and development of at least one finished artwork are documented in their Visual Arts journal.
Students investigate how artists use art elements and art principles to develop aesthetic qualities and style in an artwork. Working in their Visual Arts journal they begin to discover and understand how each of the art elements and art principles can be combined to convey different emotions and expression in their own and others’ artworks. They also explore how art elements and art principles create visual language in artworks.
Students begin to understand how exhibitions are planned and designed and how spaces are organised for exhibitions. They also investigate the roles associated with the planning of exhibitions and how artworks are selected and displayed in specific spaces. This offers students the opportunity to engage with exhibitions, whether they are in galleries, museums, other exhibition spaces or site-specific spaces.
ASSESSMENT
1. Folios (65%)
2. Research (15%)
3. Examination (20%)
YEAR 11 : Finished Works examples
Unit 3: Semester 1 – Collect, extend and connect
In this unit students are actively engaged in art making using materials, techniques and processes. They explore contexts, subject matter and ideas to develop artworks in imaginative and creative ways. They also investigate how artists use visual language to represent ideas and meaning in artworks. The materials, techniques and processes of the art form the students work with are fundamental to the artworks they make.
Students use their Visual Arts journal to record their art making. They record their research of artists, artworks and collected ideas and also document the iterative and interrelated aspects of art making to connect the inspirations and influences they have researched. The Visual Arts journal demonstrates the students’ exploration of contexts, ideas and subject matter and their understanding of visual language. They also document their exploration of and experimentation with materials, techniques and processes. From the ideas documented in their Visual Arts journal, students plan and develop artworks. These artworks may be made at any stage during this unit, reflecting the students’ own ideas and their developing style.
In order to receive constructive feedback on the progress of their art making, and to develop and extend their ideas, students present a critique of their artworks to their peer group. Students show a selection of their developmental work and artworks from their Visual Arts journal in their presentation. After the critique students evaluate their work and revise, refine and resolve their artworks.
Students will visit an exhibition in either a gallery, museum, other exhibition space or site-specific space. They must visit or view a minimum of two exhibitions during the current year of study. Exhibitions studied must be from different art spaces, to give students an understanding of the breadth of artwork in current exhibitions and to provide a source of inspiration and influence for the artworks they make. Students must select one exhibition space for study in Unit 3 and a different exhibition space for study in Unit 4. Students research the exhibition of artworks in these exhibition spaces and the role a curator has in planning and writing information about an exhibition.
Unit 4: Semester 2 – Consolidate, present and conserve
In this unit students make connections to the artworks they have made in Unit 3, consolidating and extending their ideas and art making to further refine and resolve artworks in – specific art forms. The progressive resolution of these artworks is documented in the student’s Visual Arts journal, demonstrating their developing technical skills in a specific art form as well as their refinement and resolution of subject matter, ideas, visual language, aesthetic qualities and style. Students also reflect on their selected finished artworks and evaluate the materials, techniques and processes used to make them.
The Visual Arts journal in Unit 4 includes:
- the continued development of the student’s own art making in a specific art form
- evaluation of art making in a specific art form
- the visual documentation of the processes used for finalising artworks
- annotations to support visual documentation
- research into the connections between specific artists and artworks and the student’s own artworks
- research about the presentation of artworks in exhibitions
- research undertaken for conservation and care of artworks
- research about the selection of artworks for display and the planning of exhibitions
- written and visual research to make connections with specific artists and artwork.
The progress of individual student artworks is an important element of Unit 4, and throughout the unit students demonstrate their ability to communicate to others about their artworks. They articulate the development of subject matter, ideas, visual language, their choice of materials, their understanding of the inherent characteristics and properties of the material, their use of techniques and processes, and aesthetic qualities. Acting on their critique from Unit 3, students further develop their ideas and broaden their thinking to make new artworks.
Students organise the presentation of their finished artworks. They make decisions on how their artworks will be displayed, the lighting they may use, and any other considerations they may need to present their artworks. Students also present a critique of their artworks and receive and reflect on feedback.
Students continue to engage with galleries, museums, other exhibition spaces and site-specific spaces and examine a variety of exhibitions. They review the methods used and considerations involved in the presentation, conservation and care of artworks, including the conservation and care of their own artworks. Students must visit or view a minimum of two exhibitions during the current year of study. They document the investigation and review of artworks and exhibitions in their Visual Arts journal.
ASSESSMENT
1. School-assessed Coursework – Unit 3 (5%)
2. School-assessed Coursework – Unit 4 (5%)
3. School-assessed Task – Units 3 and 4 (60%)
4. End-of-year examination – (30%)
POSSIBLE FUTURE CAREER OPPORTUNTIES:
• Artist • Curator • Conservator • Gallery Director • Art Theorist/Critic • Animator • Illustrator • Craftsperson • Furniture Designer • Fashion designer • Art Therapist • Cartoonist • Sculptor • Art Teacher • Commercial Artist e.g. Photographer, Illustrator or Concept Artist, as well as a range of careers which require problem solving and creative abilities.
Year 12 : Finished Works examples
Media
Prerequisites
There are no prerequisites for entry to Units 1, 2 and 3. Students must undertake Unit 3 and Unit 4 as a sequence. Taking 10 VCD and/or 10 Photo/Film is highly advisable.
Overview
Media is a pervasive force, shaping our lives and culture on local, national, and global levels. Stories are at its core, engaging audiences and constructing narratives that represent ideas and imagination. The context of media production and consumption influences its interpretation, reflecting societal attitudes and values. Technological advancements have revolutionized media, transforming audience participation and redefining key concepts like storytelling and influence. Audiences now transcend physical boundaries and actively contribute to media creation. The rise of social media has challenged traditional media institutions, raising concerns about accountability and regulation. VCE Media examines the construction and reflection of reality by media, as well as audience engagement and production. Through critical analysis and creative projects, students develop planning, analytical, and communication skills, paving the way for further study and careers in media-related fields.
What type of projects to expect?
Folio documentation of the media production process; creation of media type products e.g. films, posters, photographs, or zines; exercises focussing on developing skills and knowledge in professional video editing software, as well as, scripting and storyboarding; analysis of films, social media sites and alike.
What future pathways there exist?
VCE Media provides pathways to tertiary courses in e.g. Film and Television Production, Multimedia Production, Scriptwriting, Journalism, Marketing and Public Relations, Media theory and criticism, Philosophy, Sociology, Politics, Professional Communications and Photography.
Course Description
Unit 1: Semester 1 – Media forms, representations and Australian stories
In this unit, students develop an understanding of audiences and the core concepts underpinning the construction of representations and meaning in different media forms. They explore media codes and conventions and the construction of meaning in media products.
Students analyse how representations, narratives and media codes and conventions contribute to the construction of the media realities that audiences read and engage with. Students gain an understanding of audiences as producers and consumers of media products. Through analysing the structure of narratives, students consider the impact of media creators and institutions on production.
Students work in a range of media forms and develop and produce representations to demonstrate an understanding of the characteristics of each media form, and how they contribute to the communication of meaning.
Students develop an understanding of the features of Australian fictional and non-fictional narratives in different media forms. They develop research skills to investigate and analyse selected narratives, focusing on the media professionals’ influence on production genre and style. They experience the voices and stories of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander creators to gain an understanding and appreciation of how their stories contribute to our cultural identity.
ASSESSMENT
1. Coursework Theory (20%)
2. Coursework Practical (40%)
3. Examination (40%)
Unit 2: Semester 2 – Narrative across media forms
Fictional and non-fictional narratives are fundamental to the media and are found in all media forms. Media industries such as journalism and filmmaking are built upon the creation and distribution of narratives constructed in the form of a series of interconnected images and/or sounds and/or words, using media codes and conventions. New media forms and technologies enable participants to design, create and distribute narratives in hybrid forms such as collaborative and user-generated content, which challenges the traditional understanding of narrative form and content. Narratives in new media forms have generated new modes of audience engagement, consumption and reception.
In this unit, students further develop an understanding of the concept of narrative in media products and forms in different contexts. Narratives in both traditional and newer forms include film, television, digital streamed productions, audio news, print, photography, games and interactive digital forms. Students analyse the influence of developments in media technologies on individuals and society; design, production and distribution of narratives in the media; and audience engagement, consumption and reception.
Students undertake production activities to design and create narratives that demonstrate an awareness of the structures and media codes and conventions appropriate to corresponding media forms.
ASSESSMENT
1. Coursework Theory (20%)
2. Coursework Practical (40%)
3. Examination (40%)
Unit 3: Semester 1 – Media narratives, contexts and pre-production
In this unit, students explore stories that circulate in society through a close analysis of a media narrative.
Narratives are defined as the depiction of a chain of events in a cause-and-effect relationship occurring in physical and/or virtual space and time in fictional and non-fictional media products. Students consider the use of codes and narrative conventions to structure meaning and explore the role these play in media narratives. Through the close analysis of a media narrative, students develop media language and terminology and a deeper understanding of how codes and narrative conventions are combined in a narrative. They study how social, historical, institutional, culture, economic and political contexts may influence the construction of media narratives and audience readings.
Through the study of a media narrative, students explore specific codes and narrative conventions and begin the process of research to support their understanding of how they can adopt and employ these techniques in their own works. They investigate a media form that aligns with their interests and intent, developing an understanding of the codes and narrative conventions appropriate to audience engagement, consumption and reception within the selected media form. Students use the pre-production stage of the media production process to design the production of a media product for a specified audience. They explore and experiment with media technologies to develop skills in their selected media form, and reflect on and document their progress. Students undertake pre-production planning appropriate to their selected media form and develop written and visual planning documents to support the production and post-production of a media product in Unit 4.
Unit 4: Semester 2 – Media production; agency and control in and of the media
In this unit students focus on the production and post-production stages of the media production process, bringing the pre-production plans created in Unit 3 to their realisation. Students refine their media production in response to feedback and through personal reflection, documenting the iterations of their production as they work towards completion.
The context in which media products are produced, distributed and consumed is an essential framework through which audiences view and read media products. Social, historical, institutional, cultural, economic and political contexts can be seen through explicit or implied views and values conveyed within media products. The media disseminate these views and values within a society and, as a result, can play a key role in influencing, reinforcing or challenging the cultural norms.
In this unit, students view a range of media products that demonstrate a range of values and views, and they analyse the role that media products and their creators play within the contexts of their time and place of production.
Students explore the relationship between the media and audiences, focusing on the opportunities and challenges afforded by current developments in the media industry. They consider the nature of communication between the media and audiences, explore the capacity of the media to be used by governments, institutions and audiences, and analyse the role of the Australian government in regulating the media.
ASSESSMENT
1. School-assessed Coursework – Units 3 and 4 (20%)
2. School-assessed Task – Units 3 and 4 (40%)
3. End-of-year examination – (40%)
POSSIBLE FUTURE CAREER OPPORTUNTIES:
• Actor • Journalist • Arts Administrator • Make-up Artist • Audio Visual Technician • Multimedia Developer • Camera Operator • Projectionist • Copywriter • Scriptwriter • Desktop Publisher • Set Designer • Film and TV Editor • Sound Mixer • Film and TV Lighting Operator • Sound Technician • Film and TV Producer • Stage Manager • Film Critic • Web Designer/Developer • Media Teacher
YEAR 11 : Finished Works examples
YEAR 12 : Finished Works examples
Music
Prerequisites
Whilst there are no prerequisites studies for entry to Units 1, 2 and 3, students are required to be enrolled in private instrumental lessons. Students must also undertake Unit 3 and Unit 4 as a sequence.
Course Description
The new VCE Music study design is based on active engagement in all aspects of music. Students develop and refine musicianship skills and knowledge and develop a critical awareness of their relationship with music as listeners, performers, creators and music makers. Students explore, reflect on and respond to the music they listen to, create and perform. They analyse and evaluate live and recorded performances, and learn to incorporate, adapt and interpret musical practices from diverse cultures, times and locations into their own learning about music as both a social and cultural practice. Students study and practise ways of effectively communicating and expressing musical ideas to an audience as performers and composers, and respond to musical works as an audience. The developed knowledge and skills provide a practical foundation for students to compose, arrange, interpret, reimagine, improvise, recreate and critique music in an informed manner.
In this study students are offered a range of pathways that acknowledge and support a variety of student backgrounds and music learning contexts, including formal and informal.
Structure
The study is made up of ten units. Each unit deals with specific content contained in areas of study and is designed to enable students to achieve a set of outcomes for that unit. Each outcome is described in terms of key knowledge and key skills.
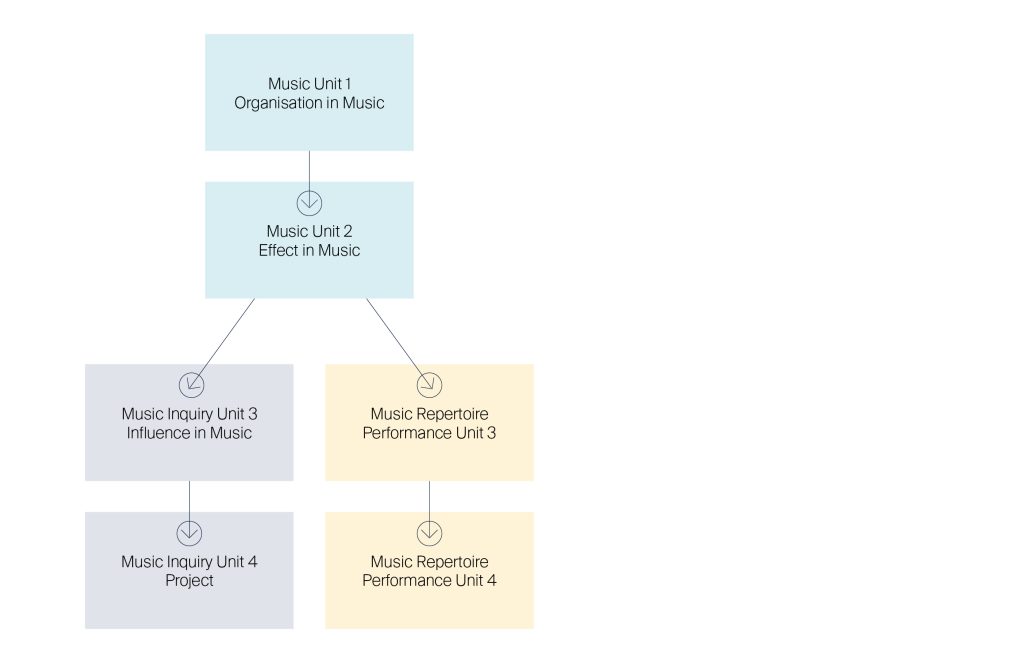
Overview: Year 11 VCE Music Units 1 & 2
Unit 1: Semester 1 – Organisation of Music
- Area of Study 1 – Performing
- Area of Study 2 – Creating
- Area of Study 3 – Analysing and responding
- Assessment – performances, composition/improvisation exercises and aural, oral, written and practical tasks.
Unit 2: Semester 2 – Effect in Music
- Area of Study 1 – Performing
- Area of Study 2 – Creating
- Area of Study 3 – Analysing and responding
- Assessment – performances, composition/improvisation exercises and aural, oral, written and practical tasks.
OVERVIEW: Year 12 VCE Music Units 3 & 4
There are two different elective pathways to choose from in Units 3 & 4 (Year 12). These are:
- Music Inquiry
- Music Repertoire performance
Music Inquiry Units 3 & 4
Unit 3: Semester 1 – Influence in Music
- Area of Study 1 – Music Making
- Area of Study 2 – Analysing for music making
- Area of Study 3 – Responding
Unit 4: Semester 2 – Project
- Area of Study 1 – Music Making
- Area of Study 2 – Analysing for music making
- Area of Study 3 – Responding
ASSESSMENT
- Unit 3 School-assessed coursework: 30%
- Unit 4 School-assessed coursework: 5%
- Externally-assessed task: 50%
- End-of-year examination: 15%
Music repertoire performance Units 3 & 4
Unit 3: Semester 1 – Music repertoire performance
- Area of Study 1 – Performing
- Area of Study 2 – Analysing for performing
- Area of Study 3 – Responding
Unit 4: Semester 2 – Music repertoire performance
- Area of Study 1 – Performing
- Area of Study 2 – Analysing for performing
- Area of Study 3 – Responding
ASSESSMENT
- Unit 3 School-assessed coursework: 20%
- Unit 4 School-assessed coursework: 10%
- Unit 4 Performance examination: 50%
- End-of-year aural and written examination: 20%
Theatre Studies
Nil.
Course Description
VCE Theatre Studies develops students’ analytical, evaluative and critical thinking, alongside expressive, collaborative and communication skills. Students work individually and in ensembles to interpret scripts, build aesthetic awareness, and understand theatre production processes—from dramaturgy to design and direction. The course cultivates an appreciation of theatre as an art form and equips students with skills for tertiary study or vocational pathways in performance, writing, design, directing, or related creative industries.
Units
Unit 1: History of Theatre Styles and Conventions (pre1945)
Students explore at least three distinct premodern theatre traditions prior to 1945, studying their conventions, staging methods and historical contexts. Working with scripts, they apply dramaturgical research and production techniques (planning, development, performance) to create scenes that demonstrate stylistic understanding. They also attend live performances and analyse how composition elements convey meaning.
Unit 2: Contemporary Theatre Styles and Conventions (1920s–present)
Students investigate at least three modern theatre styles from the 1920s to now—such as Brechtian, physical theatre, or multimedia performance. Through script work, they apply acting, direction and design concepts, integrating safe working practices. Live performance analysis strengthens their appreciation for theatre technologies, production innovation, and performance analysis skills.
Unit 3: Producing Theatre
Focusing on planning, development, and presentation stages, students produce an interpretation of a full script. Each student specialises in two production roles—such as acting and design or direction and lighting—and works cooperatively to realise their vision. They also analyse how their roles inform and elevate performance in unfamiliar scripts.
Unit 4: Presenting an Interpretation
Students study a prescribed scene and monologue from a performance text. They collaboratively interpret the scene, then individually develop a monologue interpretation either as actor/director or designer. This includes creating an Interpretation Statement and supporting design or performance choices. Monologue exams follow VCAA format, with strict timing and production role criteria.
Assessment
(Units 3 & 4)
- School-Assessed Coursework (Units 3 & 4): 45%
- End-of-Year Monologue Performance Exam: 25%
- End-of-Year Written Examination: 30%
Key Features of the 2025 Study Design
- Live Theatre Engagement: Students attend and analyse live performances, applying insights to their own work (Units 1–4)
- Professional Practice Emphasis: Structured around planning, development, and presentation stages of professional production
- Contemporary Relevance: Enhanced focus on modern and emerging theatre practices, dramaturgy, safe and ethical production, and inclusion
VCE/VET – Certificate III in Music (Performance) CUA30920
Prerequisites
Year 10 Music or Music Technology highly recommended.
Course Description
VCE/VET Music Industry is an exciting new inclusion into the academic programme at Geelong Grammar School and will offer students a whole range of practical skills related to the Music Industry. Students will be able to undertake competency-based training and assessment, while receiving a study score that contributes to their ATAR.
CUA30920 Certificate III in Music (Performance) is offered to students under the auspices of the College of Sound and Music Production (RTO #41549). This qualification is for those students who have an interest in music and are keen to develop skills as a musician with the aim to perform and compose music.
Music Performance Specialisation provides students with the opportunity to apply a broad range of knowledge and skills in varied work contexts in the music industry. Depending on the electives chosen, students will work towards composing simple songs or musical pieces and preparing for performances, whilst developing improvisation skills, applying knowledge of genre to music making and performing music as part of a group or as a soloist. Students will gain competencies that will enhance their employment opportunities within the music industry and a recognised qualification that will assist them in making a more informed choice when considering vocational/career pathways.
Units of Competence for Performance
Core Units (Year 11 only)
- CUACMP311 Implement copyright arrangements
- CUAIND313 Work effectively in the music industry
- CUAIND314 Plan a career in the creative arts industry
Elective Units (Year 11 only)
- CUAMPF213 Perform Simple Repertoire in Ensembles
- CUAMCP311 Create simple musical compositions
- CUAMPF314 Make Music Demos
- CUAMCP211 Incorporate technology into music making
- CUAMCP312 Write song lyrics
- CUASOU212 Perform basic sound editing
Elective Units (Year 12 only)
- CUAMPF312 Prepare for musical performances
- CUAMPF315 Develop and perform musical improvisation
- CUAMPF311 Develop technical skills for musical performances
- CUAMPF412 Develop and apply stagecraft skills
And choose one from the following:
- CUAMPF414 Perform music as part of a group (for bands)
- CUAMPF416 Perform music as a soloist (for soloists)
Competency Based Assessment
Competency-based training is a method of training that focuses on a learner’s ability to receive, respond to and process information in order to achieve competency. It is geared towards the attainment and demonstration of skills to meet industry-defined standards, rather than to a learner’s achievement relative to that of others.
In year 11, students will be assessed as either competent or not competent for each Unit of Competency
In year 12, students will be assessed as either competent or not competent for each Unit of Competency and in addition, students work is graded via three internal Scored Assessed Courswork tasks (SACs) and one external examination.
CONTRIBUTION TO VCE/VCAL
VCE: Students who complete Certificate III in Music Industry will be eligible for up to five Units of credit towards their VCE: up to three at the Unit 1 & 2 level and a Unit 3 & 4 sequence.
VCAL: This program contributes to the Industry Specific Skills Strand and may also contribute to the Work- Related Skills Strand of VCAL
ATAR: Students wishing to receive an ATAR contribution for the Unit 3 & 4 sequence must undertake scored assessment for the purposes of gaining a study score. This study score can contribute directly to the primary four or as a fifth or sixth study.
PATHWAY OPTIONS
• CUA40915 Certificate IV in Music Industry
• CUA50815 Diploma of Music Industry
• CUA60515 Advanced Diploma of Music Industry
POSSIBLE FUTURE CAREER OPPORTUNTIES:
• Sound Engineer • Producer • Broadcaster
• Musician • Performer • Stage Manger
• Digital Audio Technician • Sound & Lighting Technician • Songwriter
VCE/VET – Certificate III in Music (Sound Production) CUA30920
Prerequisites
Year 10 Music or Music Technology is highly recommended.
Course Description
CUA30920 Certificate III in Music (Sound Production) is offered to students under the auspices of the College of Sound and Music Production (RTO #41549). This qualification is for students who have an interest in music and sound production and are keen to develop skills in a range of areas such as recording, mixing and sound editing.
Sound Production Specialisation provides students with the practical skills and knowledge to record, mix and edit sound sources, and operate sound reinforcement equipment for live music events. The program includes core units such as implementing copyright arrangements, performing basic sound editing and developing music industry knowledge. Elective units provide students with the opportunity to learn the essentials of audio engineering and electronic music production. Students will gain competencies that will enhance their employment opportunities within the music industry, and a recognised qualification that will assist them in making a more informed choice when considering vocational and career pathways.
Units of Competency for Sound Production
Core Units (Year 11 only)
- CUACMP311 Implement copyright arrangements
- CUAIND313 Work effectively in the music industry
- CUAIND314 Plan a career in the creative arts industry
Elective Units (Year 11 only)
Three elective units are chosen each year from the list below, in alignment with the interests of the cohort.
- CUASOU331 Undertake live audio operations
- CUASOU213 Assist with sound recordings
- CUAMCP211 Incorporate technology into music making
- CUASOU212 Perform basic sound editing
- CUALGT311 Operate basic lighting
- CUAMCP311 Create simple musical composition
- CUAMPF314 Make Music demos
Elective Units (Year 12 only)
- CUASOU306 Operate sound reinforcement systems
- CUASOU308 Install and disassemble audio equipment
- CUASOU321 Mix music in studio environments
- CUASOU317 Record and mix basic music demos
- CUASOU412 Manage audio input sources
Competency Based Assessment
Competency-based training is a method of training that focuses on a learner’s ability to receive, respond to and process information in order to achieve competency. It is geared towards the attainment and demonstration of skills to meet industry-defined standards, rather than to a learner’s achievement relative to that of others.
In year 11, students will be assessed as either competent or not competent for each Unit of Competency
In year 12, students will be assessed as either competent or not competent for each Unit of Competency and in addition, students work is graded via three internal Scored Assessed Courswork tasks (SACs) and one external examination.
CONTRIBUTION TO VCE/VCAL
VCE: Students who complete Certificate III in Music Industry will be eligible for up to five Units of credit towards their VCE: up to three at the Unit 1 & 2 level and a Unit 3 & 4 sequence.
VCAL: This program contributes to the Industry Specific Skills Strand and may also contribute to the Work- Related Skills Strand of VCAL
ATAR: Students wishing to receive an ATAR contribution for the Unit 3 & 4 sequence must undertake scored assessment for the purposes of gaining a study score. This study score can contribute directly to the primary four or as a fifth or sixth study.
PATHWAY OPTIONS
• CUA40915 Certificate IV in Music Industry
• CUA50815 Diploma of Music Industry
• CUA60515 Advanced Diploma of Music Industry
POSSIBLE FUTURE CAREER OPPORTUNTIES:
• Sound Engineer • Producer • Broadcaster
• Musician • Performer • Stage Manger
• Digital Audio Technician • Sound & Lighting Technician • Songwriter
Visual Communication Design
Prerequisites
There are no prerequisites for entry to Units 1, 2 and 3. Students must undertake Unit 3 and Unit 4 as a sequence. Taking 10 VCD and/or 10 Photo/Film is highly advisable.
Overview
VCE Visual Communication Design focuses on visual language’s role in communication, problem-solving, and behaviour influence. Students manipulate type and imagery for specific purposes, audiences and contexts, combining manual and digital methods with with design elements and principles. They learn how aesthetics contribute to effective communication and design resolution. Students explore how designers visually communicate concepts in messages, objects, environments, and interactive experiences. They address design problems to improve services, systems, spaces, and places, using the design process, thinking strategies, drawings, models, and prototypes. Students participate in critiques considering factors like good design, aesthetics, and socio-cultural influences. Human-centered, ethical, sustainable, and culturally appropriate practices are considered. The study aims to nurture future-ready designers by providing them with the knowledge, skills and dispositions required of a multidisciplinary designer who is a reflective, responsible and empathetic practitioner equipped with agency and initiative.
What type of projects to expect?
Folio documentation of the design process; creation of finished designs e.g. brands, logos, illustrations, posters, flyers, brochures, visual merchandising, publications, signage, displays, objects, packaging, aps, icons, websites, visual interfaces, products, interiors, buildings and other structures; exercises focussing on developing skills and knowledge in observational and technical drawings, as well as, professional computer aided design software; visual analysis tasks.
What future pathways there exist?
VCE Visual Communication Design provides pathways to tertiary courses in design, e.g. Graphic/Communication Design, Industrial/Product Design, Architectural Design, or Advertising and Marketing; design-related studies, e.g. Mechanical, Production and/or Civil Engineering; as well as, other areas of the construction industry requiring an understanding of visual communication.
Course Description
Unit 1: Semester 1 – Finding, reframing and resolving design problems
In Unit 1 students are introduced to the practices and processes used by designers to identify, reframe and resolve human-centred design problems. They learn how design can improve life and living for people, communities and societies, and how understandings of good design have changed over time. Students learn the value of human-centred research methods, working collaboratively to discover design problems and understand the perspectives of stakeholders. They draw on these new insights to determine communication needs and prepare design criteria in the form of a brief.
This process of discovery introduces students to the phases of the VCD design process and to the modes of divergent and convergent thinking. Students integrate these ways of thinking and working into future design projects, together with their newly evolved conceptions of good design across specialist fields.
Unit 1 focus on the design of messages and objects, while introducing the role of visual language in communicating ideas and information. Students participate in critiques by sharing ideas in progress and both delivering and responding to feedback. They learn to apply the Develop and Deliver phases of the VCD design process and use methods, media and materials typically employed in the specialist fields of communication and industrial design. Student projects invite exploration of brand strategy and product development, while promoting sustainable and circular design practices. Lastly, students also consider how design decisions are shaped by economic, technological, cultural, environmental and social factors, and the potential for design to instigate change.
ASSESSMENT
1. Folios (75%)
2. Examination (25%)
Unit 2: Semester 1 – Design contexts and connections
This unit builds on understandings of visual communication practices developed in Unit 1. Students draw on conceptions of good design, human-centred research methods and influential design factors as they revisit the VCD design process, applying the model in its entirety. Practical tasks across the unit focus on the design of environments and interactive experiences. Students adopt the practices of design specialists working in fields such as architecture, landscape architecture and interior design, while discovering the role of the interactive designer in the realm of user-experience (UX). Methods, media and materials are explored together with the design elements and principles, as students develop spaces and interfaces that respond to both contextual factors and user needs.
Student learning activities highlight the connections between design and its context, and the emotive potential of interactive design experiences in both physical and digital spaces. Students also look to historical movements and cultural design traditions as sources of inspiration, and in doing so consider how design from other times and places might influence designing for the future. Design critiques continue to feature as an integral component of design processes, with students refining skills in articulating and justifying design decisions, and both giving and receiving constructive feedback.
Connections between design, time and place are also central to the study of culturally appropriate design practices in Area of Study 2. Students learn about protocols for the creation and commercial use of Indigenous knowledge in design, with a particular focus on Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander design traditions and practices. Students also consider how issues of ownership and intellectual property impact the work of designers across contexts and specialist fields.
ASSESSMENT
1. Folios (75%)
2. Examination (25%)
Unit 3: Semester 1 – Visual communication in design practice
In this unit students explore and experience the ways in which designers work, while also analysing the work that they design. Through a study of contemporary designers practising in one or more fields of design practice, students gain deep insights into the processes used to design messages, objects, environments and/or interactive experiences. They compare the contexts in which designers work, together with their relationships, responsibilities and the role of visual language when communicating and resolving design ideas. Students also identify the obligations and factors that influence the changing nature of professional design practice, while developing their own practical skills in relevant visual communication practices.
Students study not only how designers work but how their work responds to both design problems and conceptions of good design. They interrogate design examples from one or more fields of design practice, focusing their analysis on the purposes, functions and impacts of aesthetic qualities. This exposure to how, why and where designers work, what they make and the integral role of visual language in design practice provides the foundation for students’ own investigation of the VCD design process.
Students explore the Discover, Define and Develop phases of the VCD design process to address a selected design problem. In the Discover and Define phases, research methods are used to gather insights about stakeholders and a design problem, before preparing a single brief for a real or fictional client that defines two distinct communication needs. Students then embark on the Develop phase of the VCD design process, once for each communication need. They generate, test and evaluate design ideas and share these with others for critique. These design ideas are further developed in Unit 4, before refinement and resolution of design solutions.
Unit 4: Semester 2 – Delivering design solutions
In this unit students continue to explore the VCD design process, resolving design concepts and presenting solutions for two distinct communication needs. Ideas developed in Unit 3, Outcome 3 are evaluated, selected, refined and shared with others for further review. An iterative cycle is undertaken as students rework ideas, revisit research and review design criteria defined in the brief. Manual and digital methods, media and materials are explored together with design elements and principles, and concepts tested using models, mock-ups or low-fidelity prototypes.
When design concepts are resolved, students devise a pitch to communicate and justify their design decisions, before responding to feedback through a series of final refinements. Students choose how best to present design solutions, considering aesthetic impact and the communication of ideas. They select materials, methods and media appropriate for the presentation of final design solutions distinct from one another in purpose and presentation format, and that address design criteria specified in the brief.
ASSESSMENT
1. School-assessed Coursework – Unit 3 (20%)
2. School-assessed Task – Units 3 and 4 (50%)
3. End-of-year examination – (30%)
POSSIBLE FUTURE CAREER OPPORTUNTIES:
• Animation Designer • Architect • Concept Designer • Fashion Designer • Graphic Designer • Illustrator • Industrial/Product Designer • Interior Designer • Landscape Architect • Multimedia Designer • Set/Stage Designer • UX/UI designer • Web Designer/Developer
